(Nanowerk Information) Transition steel selenides have been thought-about to be a sensible choice for electrocatalytic water splitting. As well as, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have been used to make catalysts with good electrocatalytic capabilities. Historically, the MOF-derived selenides are produced through the self-sacrificing MOF template strategies. Nevertheless, this technique is high-energy consuming, and it’s tough to exactly management the construction and element homogeneity of the product throughout pyrolysis.
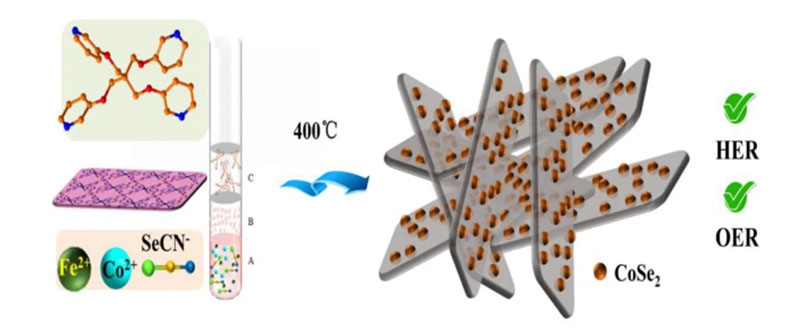
This work reveals that the rational design of layered MOFs with S- or Se-containing linkers as water splitting catalysts is a possible possibility for the event of economical and low-energy-consuming electrocatalysts. In the meantime, it offers an revolutionary method for the synthesis of MOF-based metallic selenides.







