Vaccines and therapies primarily based on messenger RNA might be extra readily delivered resulting from a non-toxic polymer that protects RNA and controls its launch inside cells.
The arrival of vaccines utilizing messenger RNA (mRNA) to direct immunogenic protein synthesis, best-known in vaccines towards COVID-19, is stimulating researchers to seek out higher methods to maintain the mRNA secure and ship it successfully.
A group on the College of Tokyo, with collaborators in Japan and China, has now developed polymers that may work together with, stabilize and encase mRNA, permitting extremely efficient supply into cultured human cells and cells of reside mice. They’ve published their work within the journal Science and Technology of Superior Supplies.
“Past vaccines for infectious diseases, mRNA presents promising avenues for unprecedented remedies like protein substitute therapies, gene enhancing, and immunotherapies,” says Horacio Cabral of the College of Tokyo group. “However to unlock the complete potential of those superior therapies, the event of protected and efficient provider techniques is paramount.”
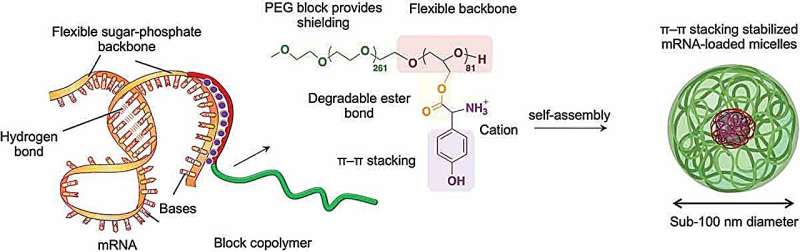
The researchers investigated methods to fine-tune the construction of their polymer molecules to permit them to work together with mRNA to guard it. The biocompatible and non-toxic polymers had been of a sort referred to as block-copolymers, constructed from alternating segments of various chemical teams, on this case polyethylene glycol and polyglycerol.
However the important thing to attaining applicable interplay with mRNA was to connect particular positively charged amino acid teams to the lengthy polymer spine. The constructive cost typically attracts the polymer to negatively charged RNA, and the chosen amino acids had been additionally capable of work together with components of the mRNA in a course of referred to as pi–pi (π–π) stacking. This entails interactions between electrons in a characteristic referred to as pi bonds in cyclic molecular rings stacked aspect by aspect within the interacting molecules.
“It is a extremely customizable strategy, permitting fine-tuning of our polymer’s interactions with mRNA,” says Cabral. Because of this, the mRNA was stabilized extremely successfully, overcoming a significant downside of instability discovered with various approaches.
The polymer and mRNA spontaneously assembled into spherical bundles—micelles—that successfully delivered the mRNA cargo into cultured cells and in addition into mouse cells after intramuscular injection. The mRNA was readily launched inside cells to generate the proteins it encoded at excessive effectivity, and for a considerably longer time than various approaches.
“This work was very difficult as a result of delicate nature of mRNA, a extremely fragile molecule that wants safety outdoors target cells however rapid publicity to the cell equipment as soon as inside,” says Cabral. He provides, “Our success is thrilling resulting from its potential to remodel mRNA supply applied sciences, permitting exact engineering, modern launch methods, and overcoming essential obstacles to boost stability and efficacy in mRNA-based therapies.”
Extra info:
Wenqian Yang et al, Block catiomers with flanking hydrolyzable tyrosinate teams improve in vivo mRNA supply through π–π stacking-assisted micellar meeting, Science and Technology of Superior Supplies (2023). DOI: 10.1080/14686996.2023.2170164
Offered by
National Institute for Materials Science
Quotation:
Stabilizing mRNA vaccines for supply to cells (2024, February 16)
retrieved 16 February 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-02-stabilizing-mrna-vaccines-delivery-cells.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.







