A nonprofit has launched the primary open supply platform aimed toward delivering refined anti-fraud capabilities to monetary programs in Africa in addition to elements of Asia and the Center East.
The Tazama open supply venture is real-time monetary transaction monitoring software program that may be deployed by digital monetary providers suppliers to detect and block fraudulent transactions and defend client accounts. Whereas massive monetary companies resembling Visa and Mastercard have such capabilities, smaller monetary establishments and authorities businesses within the area don’t, making their monetary programs vulnerable to fraud and undermining residents’ belief within the system.
Funded by the Linux Basis Charities and the Invoice and Melinda Gates Basis, the open source Tazama project has accomplished alpha pilot tasks in Jordan and South Africa and plans to broaden its deployments. It is already working with the Central Financial institution of West African States (BCEAO) and rural banks within the Philippines, says Greg McCormick, government director of the Tazama Undertaking at Linux Basis.
“What we wish is a system that’s inexpensive, simple to make use of, and may deal with sure sorts of fraud,” he says. “We’re making an attempt to essentially serve the underserved, if you’ll, and get them banked and get them into the into the longer term and hopefully assist them” get to a spot the place they’re incomes greater than {dollars} a month, he provides.
Offering anti-fraud providers like Tazama is crucial to increasing trust and elevating residents’ participation in a rustic’s monetary system, which is a key a part of general financial improvement. Africa and a few nations within the Center East and Asia lag far behind in account possession in contrast with america, Europe, and the richer economics of Asia. Solely 27% of adults in Egypt have a checking account, 47% of adults in Jordan, 45% in Kenya, 36% in Burkina Faso, and 45% in Nigeria, based on The Global Findex Database 2021, printed by the World Financial institution.
The Gates Foundation found that delivering banking providers to lower-income residents is a key part of assembly its objective of serving to deploy real-time digital funds, which may also help economies develop. In lots of international locations, individuals are dwelling on simply {dollars} a month, which doesn’t make it worthwhile for giant monetary companies to create their very own monetary networks. As an alternative, homegrown programs primarily based on open supply software program are wanted, McCormick says.
Actual-Time Fraud Detection
The Tazama open supply software program is a server that takes in data and applies greater than 270 completely different guidelines, every one in all which produces a single reply. The principles are mixed into typologies, which search for specific sorts of fraud, based on Tazama documentation.
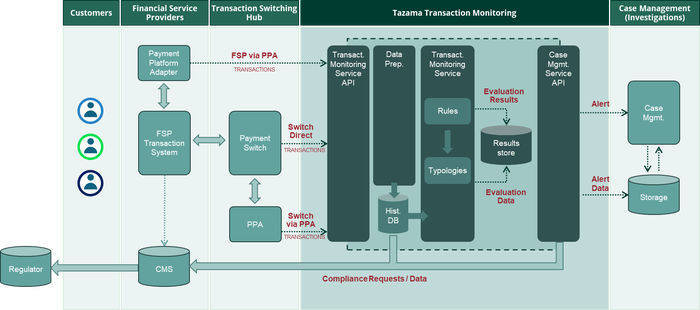
The knowledge movement for a monetary transaction in Tazama’s anti-fraud platform. Supply: Tazama.org
With digital fraud rising in Africa and different elements of the world, resembling a recent spate of Magecart attacks on e-commerce web sites, defending the monetary system and its members from fraud is very well timed.
The pilot venture’s servers are presently operating 2,300 transactions per second, which ends up in detection of fraud in real-time, McCormick says.
“We’re hardening the community, so fewer locations for individuals to get on board and do dangerous issues — much less cash muling and points alongside these strains,” he says. “We provide about 30 sorts of fraud checks proper now, however to be sincere, all people that makes use of this technique goes to customise it.”
For instance, the Central Financial institution of West African States (BCEAO) — made up of greater than 270 banks, 17 cell cash operations, and 43 cash “creators” — will probably mandate that these organizations have an anti-fraud functionality and end in about 60% to 70% of these organizations utilizing Tazama, he says.
Including AI for Cybersecurity
The platform is a machine-learning engine that ingests transaction knowledge in real-time, shops the knowledge in a database, after which makes use of behavioral modeling to find out whether or not the transaction is probably going professional or an indication of fraud, says Justus Ortlepp, product supervisor for Tazama.
“The intention is for the platform to have the ability to ingest your entire transactions in order that it will probably have as complete an image of any person’s habits,” he says. “That ‘any person’ might be an organization, authorized entity that’s buying and selling throughout the community, or a person who’s utilizing the monetary system.”
Tazama additionally targets different sorts of monetary ruses. Job fraud, the place the prison gives work to individuals however then steals their cash, is frequent in some elements of Africa, whereas laundering funds stolen by different prison schemes is one other frequent assault on monetary programs, says Ortlepp.
“Despite the fact that cash laundering just isn’t usually fraud, fraud finally turns into cash laundering anyway, as a result of that is how fraudsters squirrel away their funds and conceal the proceeds of that exact crime,” he says.
The Tazama group plans to construct extra capabilities into the platform, together with explainable AI and different superior options. Many focused international locations should not have a cybersecurity-skilled workforce or assets to deploy a posh platform, so utilizing machine studying and AI to make the platform simpler to make use of and handle is vital, McCormick says.
“We have to make it fairly easy, in order that the banks and fintechs and the opposite individuals may run this and may create trusted networks and do belief transactions,” he says. “So the longer term is absolutely all about simplification, using AI and including extra performance so far as ease of use.”







