Ever because the Web grew to become a business entity, hackers have been utilizing it to impersonate companies by way of a wide range of intelligent means. And probably the most enduring of those exploits is the observe of typosquatting — i.e., utilizing look-alike web sites and domains to lend legitimacy to social engineering efforts.
These look-alikes prey on customers’ inattention to verifying respectable web sites, and typically depend on human errors, equivalent to coming into a typo in a URL, to seize victims. A few of these domains have small deliberate spelling errors, including a hyphen or substituting similar-looking characters; one of many early typosquatted domains, as an illustration, was Goggle.com, which was shortly taken down when it was found by Google.
However despite the fact that the tactic has been round for many years, attackers are getting extra subtle and studying learn how to higher disguise their faux domains and messages to be simpler in spreading their malware and stealing knowledge and funds from inattentive customers.
Typosquatting Assaults on the Rise
Typosquatting’s continued prevalence was most just lately demonstrated by a worrying spike in Bifrost Linux malware variants through the previous few months that use faux VMware domains. However there are numerous different latest examples of typosquatting assaults too.
These embrace the emergence of rip-off websites that rely on brand impersonation, a spate of fake job hiring websites, phishing efforts from the SolarWinds supply chain attackers again in 2022, and crooks misusing X’s for-pay badge system in 2023, amongst many others.
Renée Burton, head of menace intelligence at Infoblox, has been monitoring these criminals. Infoblox’s telemetry — which analyzes billions of community knowledge factors every day — spots greater than 20,000 such domains weekly.
“The actual menace to customers and enterprises globally comes from crafted lookalike domains, which means there is no such thing as a accident concerned,” she explains. “A felony is making a deliberate option to attempt to idiot somebody. They are often very convincing to a consumer and are exhausting to identify, particularly in small browser fonts. Lots of them go unnoticed.”
Typosquatting criminals are consistently refining their craft in what appears to be a unending cat and mouse battle. A number of years in the past, researchers discovered the homograph ploy, which substitutes non-Roman characters which can be exhausting to differentiate after they seem on display screen. For instance, as a substitute of utilizing “apple.com” in a URL, a felony will assemble its homograph with the code “xn–80ak6aa92e.com,” which leverages Cyrillic characters as a substitute. Since then, all fashionable browsers have been up to date to acknowledge these homograph assault strategies.
In an Infoblox report from final April entitled “A Deep3r Look at Lookal1ke Attacks,” the report’s authors said that “everyone seems to be a possible goal.”
“Low cost area registration costs and the power to distribute large-scale assaults give actors the higher hand,” they wrote within the report. “Attackers have the benefit of scale, and whereas methods to determine malicious exercise have improved through the years, defenders battle to maintain tempo.”
As an example, the report exhibits an growing sophistication in using typosquatting lures: not only for phishing or easy fraud but additionally for extra superior schemes, equivalent to combining web sites with faux social media accounts, utilizing nameservers for main spear-phishing electronic mail campaigns, organising phony cryptocurrency buying and selling websites, stealing multifactor credentials and substituting respectable open-source code with malicious to contaminate unsuspecting builders.
An instance of the final merchandise is how attackers leveraged “requests,” a very talked-about Python package deal with greater than 6 million downloads each day. “Packages with names equivalent to ‘requessts,’ ‘requeests,’ ‘requuests,’ ‘reqquests,’ ‘reequests,’ and ‘rrequests’ have been noticed” by researchers at Unit42, in line with the Infoblox report.
Criminals have additionally gotten extra reactive to information occasions, equivalent to creating fake sites to take donations intended for earthquake disaster relief. And a brand new twist was just lately found by Akamai, specializing in the hospitality trade. This concerned scammers who replicated lodge reserving pages for the preliminary phishing marketing campaign, adopted up by then stealing bank card knowledge from potential visitor bookings. The criminals appended subdomain phrases equivalent to “reservation” or “help” to their squatted domains to make them seem extra plausible.
Stijn Tilborghs, the lead knowledge scientist at Akamai, says, “I’d have fallen for this explicit exploit. It’s important to be actually paranoid to suspect an assault.”
How one can Battle Typosquatting
Way back to 2014, a paper introduced at a USENIX convention by Janos Szurdi, entitled “The Long ‘Taile’ of Typosquatting Domain Names” (observe the intentional typo), discovered that in analyzing 1000’s of internet sites, together with less-visited ones, typosquatting was widespread and focused a large assortment of domains.
Szurdi discovered the observe had elevated over time and that the area squatters make investments important sources in working their felony companies. The paper maps out their ecosystem as proven beneath, together with 1) incoming visitors, 2) creating phishing pages, 3) serving up malware, and 4) redirecting to various domains and different strategies.
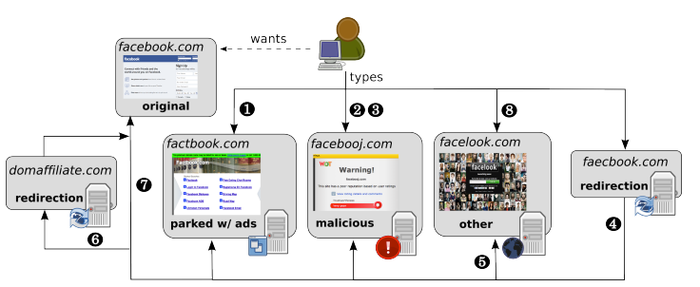
The typosquatting ecosystem with varied methods criminals can generate funds. Supply: Janos Szurdi through USENIX.
The lengthy historical past of typosquatting carries an necessary lesson for IT professionals — particularly, be careful for injection-style assaults throughout a company Net infrastructure. Each aspect of each webpage could be compromised, even hardly ever used tiny icon recordsdata. It helps to pay extra cautious consideration, particularly when shopping web sites on cellular units.
However there are a number of protecting measures that may be deployed by companies. A method is to make use of one in every of many various area identify service suppliers, equivalent to OpenDNS and Google’s DNS. These embrace typosquatting safety that acknowledges the exploit for the bigger net locations. Nevertheless, these protections cannot sustain with the 1000’s of latest typo domains registered every day.
One other suggestion is for company safety instruments for use to fastidiously assessment log entry recordsdata. And, safety consciousness coaching workouts are helpful to assist sensitize customers with varied methods to acknowledge the exploit.
“Nobody firm can catch the whole lot,” Akamai’s Tilborghs says. “You want a number of layers. And be tremendous cautious at all times. The dangerous guys have a bonus. They’ll ship an assault to 1000’s of domains, and rely on just a few of them getting by way of.”
A part of the issue, as talked about within the USENIX 2014 paper, is that “one can not simply classify a brand new registration for example of typosquatting primarily based on its identify alone.” This the place corporations equivalent to Akamai and Infoblox have deployed a mix of automated and handbook detection strategies of their instruments. Nonetheless, all it takes is one distracted worker to fall sufferer.
“Typosquatting has prompted annoyances for Web customers for a very long time. Since customers lack efficient countermeasures, speculators maintain registering domains to focus on domains and exploit the visitors arriving from mistyping these domains,” the USENIX authors wrote of their report, a press release that’s nonetheless true at the moment.







