Researchers at AIST have created a technique to introduce alkali metals into the graphene interlayers, working with researchers from Osaka College, Tokyo Polytechnic College, Kyushu College, and Nationwide Tsing Hua College. A single sheet of carbon atoms organized in a hexagonal lattice is named graphene. The atomic configuration of the implanted alkali steel atoms, which is a hexagonal close-packed bilayer construction, has been efficiently noticed by them.
The efficiency of rechargeable batteries has a big influence on the driving vary of electrical automobiles and smartphone utilization time. Enhancing the efficiency of those digital devices is achievable if rechargeable batteries can amass extra electrical energy.
Graphite, the electrode materials utilized in batteries, is made up of multilayers of graphene with alkali metals sandwiched between the layers to allow electron stream throughout charging and discharge. Attaining a excessive density of alkali steel storage between graphene layers may improve electrical capability.
X-Ray and electron diffraction experiments have made it usually recognized over the previous century that graphene interlayers can solely maintain one layer of alkali steel. The theoretical charging restrict is the variety of single-layer alkali steel atoms that fill every layer to capability.
There haven’t been any research that instantly observe the atomic association of interlayer alkali metals, although, to verify whether or not graphene layers can solely maintain a single layer of alkali steel atoms or if different strategies can produce a number of layers or a better density of alkali metals.
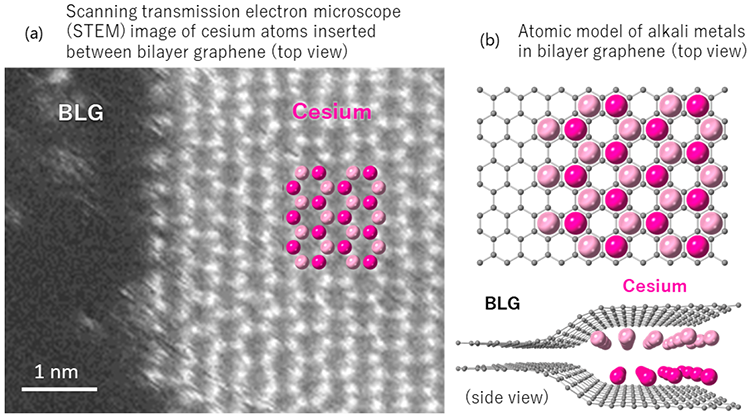
A technique for introducing dense alkali metals in between graphene layers has been devised by the researchers. They’ve efficiently noticed the association construction of alkali steel atoms between the graphene layers utilizing a high-performance low-voltage (60 kV) electron microscope.
Attributable to their versatile interlayer spacing, alkali metals are densely packed in a two-layer construction in floor layer graphite and bilayer graphene. This makes it potential to inject about twice as many alkali metals. It’s anticipated that graphene with two layers of alkali steel insertion would perform as an electrode materials to extend the capability of secondary alkaline ion batteries.
Background
Japan is making important strategic investments within the growth of rechargeable batteries to be used in electrical vehicles and data expertise to decarbonize society and create a complicated data community that hyperlinks individuals, merchandise, and companies.
The essential problem of lowering battery weight and rising battery capability is among the elemental applied sciences required to enhance the efficiency of rechargeable batteries. Carbon layers make up graphite, a robust and light-weight electrode materials.
Lithium and different alkali steel ions bear electron transfers all through the charging and discharging course of. Growing the quantity of alkali steel ions within the electrodes is important to boosting the capability of rechargeable batteries.
Nonetheless, atomic-level observations of the electrode construction have confirmed tough to perform utilizing typical strategies of measurement and evaluation. Moreover, there have been only a few design directions accessible for effectively introducing alkali steel ions into graphene layers.







