
Educational researchers developed ZenHammer, the primary variant of the Rowhammer DRAM assault that works on CPUs based mostly on latest AMD Zen microarchitecture that map bodily addresses on DDR4 and DDR5 reminiscence chips.
AMD Zen chips and DDR5 RAM modules had been beforehand thought-about much less susceptible to Rowhammer, so the most recent findings problem this notion.
The ZenHammer attack was developed by researchers at public analysis college ETH Zurich, who shared their technical paper with BleepingComputer.
Assault background
Rowhammer is a well-documented assault methodology that exploits a bodily attribute of contemporary Dynamic Random-Entry Reminiscence (DRAM) to change knowledge by repeatedly accessing (“hammering”) particular rows of reminiscence cells by way of learn/write operations to alter bit values inside.
Reminiscence cells retailer data as electrical fees that decide the worth of the bits inside as a 1 or a 0. Due to the elevated density of the reminiscence cells in fashionable chipscells, repeated “hammering” can change the cost state in adjiacent rows, a course of often called “bit flipping.”
By strategically inducing these bit flips in particular areas, an attacker might acquire entry to delicate knowledge (e.g. cryptographic keys) or escalate privileges.
The approach has been demonstrated on Intel and ARM CPUs, leaving AMD’s Zen structure CPUs largely unexplored because of inherent challenges reminiscent of unknown DRAM addressing schemes, synchronization with refresh instructions, and problem to realize a excessive sufficient row activation throughput.
With ZenHammer, the researchers at ETH Zurich managed to deal with these challenges by reverse-engineering the advanced and non-linear DRAM addressing features in AMD platforms.
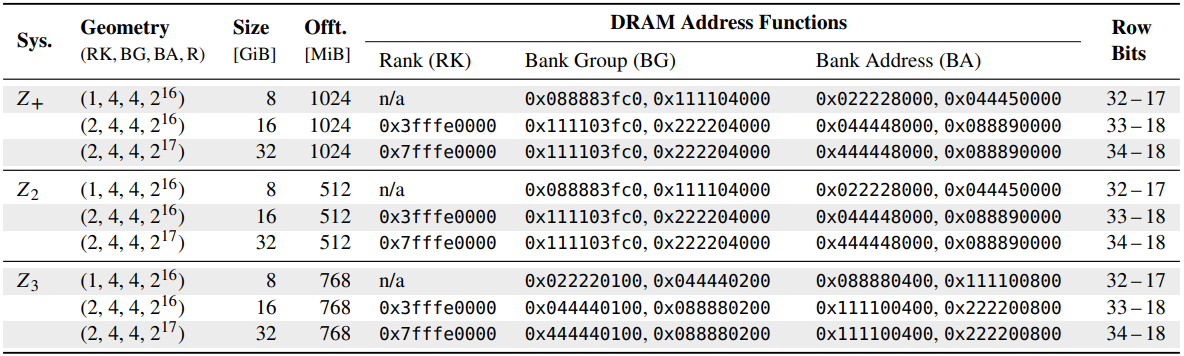
Additionally they developed novel synchronization strategies to time their assaults with DRAM’s refresh instructions, which was essential for bypassing mitigations like Goal Row Refresh (TRR).
Moreover, the researchers optimized reminiscence entry patters to extend row activation charges, which is a important issue within the success of Rowhammer assaults.
Take a look at outcomes
The researchers demonstrated that the ZenHammer assault might induce bit flips with DDR4 units on AMD Zen 2 (Ryzen 5 3600X) and Zen 3 platforms (Ryzen 5 5600G). They had been profitable in 7 out of 10 checks on DDR4/AMD Zen 2 platforms and 6 out of 10 DDR4/AMD Zen 3 platforms.
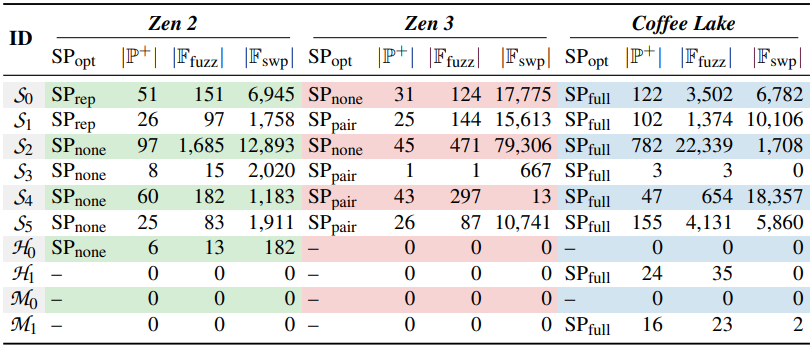
The researchers had been additionally profitable with DDR5 chips on AMD’s Zen 4 microarchitectural platform, previously considered higher shielded in opposition to Rowhammer assaults.
Nonetheless, the check was profitable on solely one of many 10 programs, a Ryzen 7 7700X, indicating “that the modifications in DDR5 reminiscent of improved Rowhammer mitigations, on-die error correction code (ECC), and a better refresh price (32 ms) make it more durable to set off bit flips.”
These bit flips weren’t simply theoretical, because the analysts had been capable of simulate profitable assaults that focused the system’s safety, together with manipulating web page desk entries for unauthorized reminiscence entry.
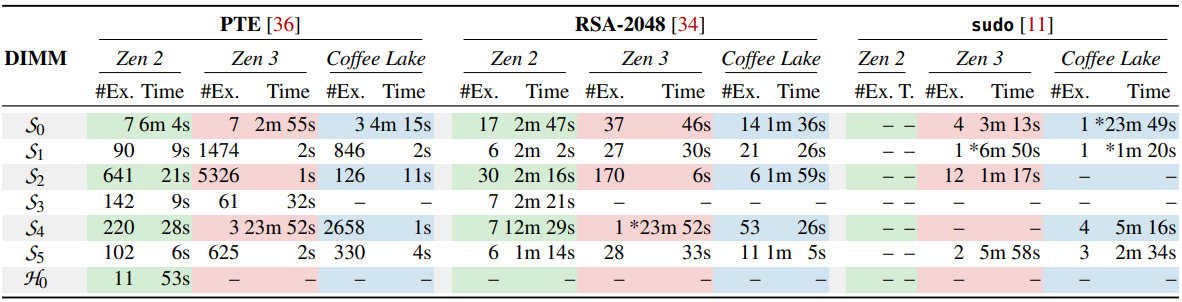
On one of many Zen 3 check programs produced in This autumn 2021, the researchers had been capable of acquire root privileges in 10 profitable assaults with a mean time of 93 seconds, beginning the second an exploitable bit flip was found.
The choices AMD CPU customers must defend in opposition to this menace resume to making use of software program patches and firmware updates. They could additionally need to think about using {hardware} that has carried out particular mitigations in opposition to Rowhammer, which usually integrates newer know-how.
It’s price highlighting that these assaults are advanced and profitable execution requires an attacker with a deep understanding of each software program and {hardware} parts.
Replace 3/25 – AMD has revealed a security bulletin in response to ZenHammer, providing mitigation recommendation and assuring that it’s assessing the problems completely and can present updates.







