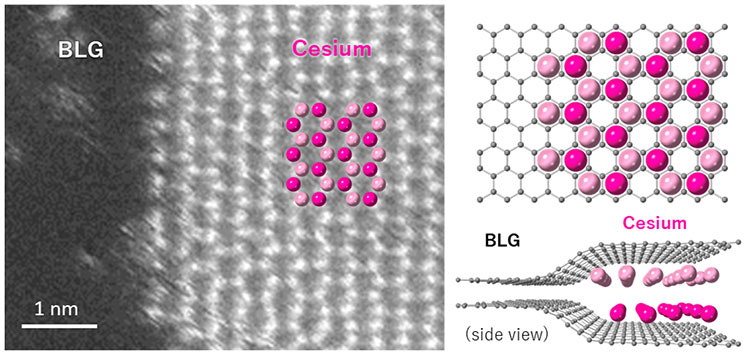
(Nanowerk Information) Researchers at AIST, in collaboration with Osaka College, Tokyo Polytechnic College, Kyushu College, and Nationwide Tsing Hua College, have developed a method to insert alkali metals into the interlayers of graphene. They’ve succeeded in immediately observing the atomic association of the inserted alkali metallic atoms which is a hexagonal shut packed bilayer construction.