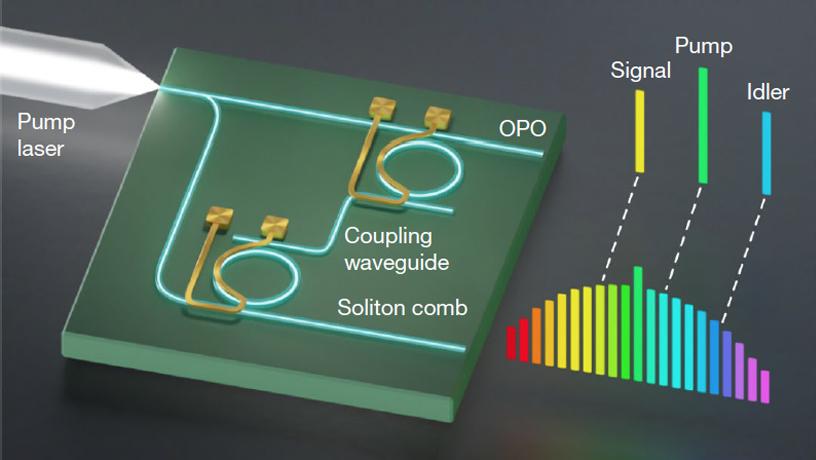
(Nanowerk Information) In a brand new Nature examine (“All-optical frequency division on-chip using a single laser”), Columbia Engineering researchers have constructed a photonic chip that is ready to produce high-quality, ultra-low-noise microwave alerts utilizing solely a single laser. The compact gadget — a chip so small, it might match on a pointy pencil level — ends in the bottom microwave noise ever noticed in an built-in photonics platform.