Whereas the US Securities and Trade Fee has printed guidelines for better cybersecurity governance for years, public firms have principally ignored them. And whereas the necessities might be tough to fulfill, corporations which have made the hassle created almost 4 instances their shareholder worth in contrast to those who have not.
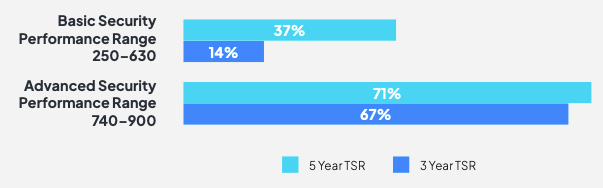
Bitsight and Diligent surveyed hundreds of public corporations, discovering a correlation between cybersecurity expertise and the typical complete shareholder return over three and 5 years. (Supply: Bitsight)
That is the conclusion of a brand new survey collectively carried out by Bitsight and Diligent Institute, entitled “Cybersecurity, Audit, and the Board.” The survey took a deep dive into greater than 4,000 midsized-to-large corporations all over the world, investigating the experience of administrators together with the backgrounds of audit and specialised danger committee members. They measured cybersecurity experience throughout 23 completely different danger elements, such because the presence of botnet infections, servers internet hosting malware, outdated encryption certificates for Net and e mail communications, and open community ports on public-facing servers.
“Boards that train cyber oversight via specialised committees with a cyber skilled member versus counting on the complete board are extra seemingly to enhance their total safety postures and monetary efficiency,” says Ladi Adefala, a cybersecurity guide and CEO of Omega315, who agrees with the report’s conclusions. He labored for a Fortune 500 firm on this challenge and located that “the board did not have a centered committee to spend the time to dig into cyber matters. In addition they did not have sufficient members and subsequently cannot afford to have specialised committees for cyber,” he says. A part of his consulting follow helps to arrange such committees, what he calls offering cyber civics classes.
Individuals assets apart, poor cybersecurity governance is not actually information: Public corporations have been giving cybersecurity quick shrift for years. For instance, safety skilled David Froud has been writing about this subject since a minimum of 2017. However what’s new is seeing how arduous it’s to evaluate cyber information and to construct enduring governance.
Based on the Bitsight report, having separate board committees centered on specialised danger and audit compliance produces one of the best outcomes. The authors wrote, “These committees are higher positioned to dive deep into particular cybersecurity points they usually can develop stronger relationships with the executives charged with the day-to-day cybersecurity operations. This, in flip, can result in higher cybersecurity-related coverage, price range and different selections being made on the board degree.”
The survey discovered a variety of cyber expertise amongst healthcare and monetary services-related corporations — which ranked the best — in contrast with industrial corporations, which ranked lowest.
What’s telling is that the overwhelming majority of corporations have carried out a poor job at integrating such specialists on their boards of administrators and committees. The report discovered that 5% of these surveyed (and 12% of the S&P 500 corporations) had these specialists on their boards. However simply having a CISO or CTO on the board is not any assure of cybersecurity efficiency. “These consultants should be built-in into current constructions” and protecting measures, Bitsight famous.
Not talked about within the report was one other governance weak spot: constructing lasting cyber resilience. This was the topic of one other survey, carried out by the Cybersecurity at MIT Sloan Analysis Consortium and published in the Harvard Business Review final 12 months. The MIT workforce surveyed 600 board members and located their interactions with CISOs are missing. Fewer than half the respondents have any common contact with their CISOs, principally restricted to displays made at board conferences and never a lot else.
In lots of instances, these displays are restricted to the mechanics of protecting measures, akin to how usually they conduct purple workforce workouts or phishing consciousness coaching. Keri Pearlson, govt director of the MIT consortium and co-author (with Lucia Milică, International Resident CISO at Proofpoint) of the HBR article, attracts an analogy with the medical world: “Once we are uncovered to an an infection, we both do not get sick, or if we do get sick, we’ve got issues in our our bodies that mechanically go to work to get us again to being higher.”
What’s wanted, she provides, is for “boards to debate their group’s cybersecurity-induced dangers and consider plans to handle these dangers.”
As Adefala sums it up, “Probably the most compelling approach is to leverage cybersecurity as a strategic asset for income creation or operational agility, slightly than as an operational necessity.”







