Malicious actors have been detected abusing the open-source hypervisor platform QEMU as a tunneling device in a cyberattack in opposition to a big firm.
QEMU is a free emulator and hypervisor that lets you run different working programs as friends on a pc.
As a part of the assault, menace actors used QEMU to create digital community interfaces and a socket-type community machine to connect with a distant server. This allowed the menace actors to create a community tunnel from the sufferer’s system to the attacker’s server with negligible influence on system efficiency.
This uncommon case, which highlights the various strategies attackers use to stay stealthy, was found by Kaspersky analysts who have been referred to as to analyze suspicious exercise within the breached firm’s programs.
Stealthy community tunnels
Hackers create community tunnels to ascertain a stealthy and safe communication channel between them and a compromised system.
Sometimes, these tunnels encrypt community site visitors to assist bypass firewalls, intrusion detection programs, and different safety measures.
Kaspersky says that in 10% of the circumstances it has investigated up to now three years, hackers have used the FRP and ngrok utilities to create tunnels. Different tunneling instruments utilized in assaults embrace CloudFlare tunnels, Stowaway, ligolo, 3proxy, dog-tunnel, chisel, gs-netcat, plink, iox, and nps.
As a consequence of their frequent abuse by cybercriminals, defenders and monitoring instruments deal with these instruments with suspicion.
On this uncommon case involving QEMU, the attackers determined to leverage a much less standard device for creating community tunnels that will unlikely elevate any alarms, even when that meant giving up site visitors encryption.
Moreover, QEMU gives distinctive capabilities reminiscent of emulating a variety of {hardware} and digital networks, permitting malicious actions to mix in with benign virtualization site visitors, and bridging segmented community elements via strategically arrange VM pivot factors.
Feather-light backdoor
Within the assault seen by Kaspersky, the hackers utilized ‘Offended IP Scanner’ for community scanning, ‘mimikatz’ for credential theft, and QEMU for creating a complicated community tunneling setup that facilitated a covert communication channel.
The attackers tried to maintain their footprint as minimal as doable, solely allocating 1MB of RAM to the digital machine they created, significantly lowering the possibilities of detection via useful resource consumption.
The configuration of the VM, which was began with out utilizing a LiveCD or disk picture, contains the next arguments:
- -netdev consumer,id=lan,prohibit=off: Configures a community backend named ‘lan’ in consumer mode, permitting unrestricted community entry via the host’s community stack.
- -netdev socket,id=sock,join=<IP>:443: Establishes a socket connection to a specified IP deal with on port 443, making a direct community hyperlink for the backend ‘sock’.
- -netdev hubport,id=port-lan,hubid=0,netdev=lan/sock: Hyperlinks a community machine (both lan or sock) to a digital hub hubid=0, facilitating community connectivity between totally different backends.
- -nographic: Runs QEMU with out a graphical interface, choosing command-line interplay solely, lowering its visibility and useful resource footprint.
Kaspersky carried out simulated checks to copy the attackers’ particular use of QEMU, concluding that the setup appeared just like the one within the diagram under.
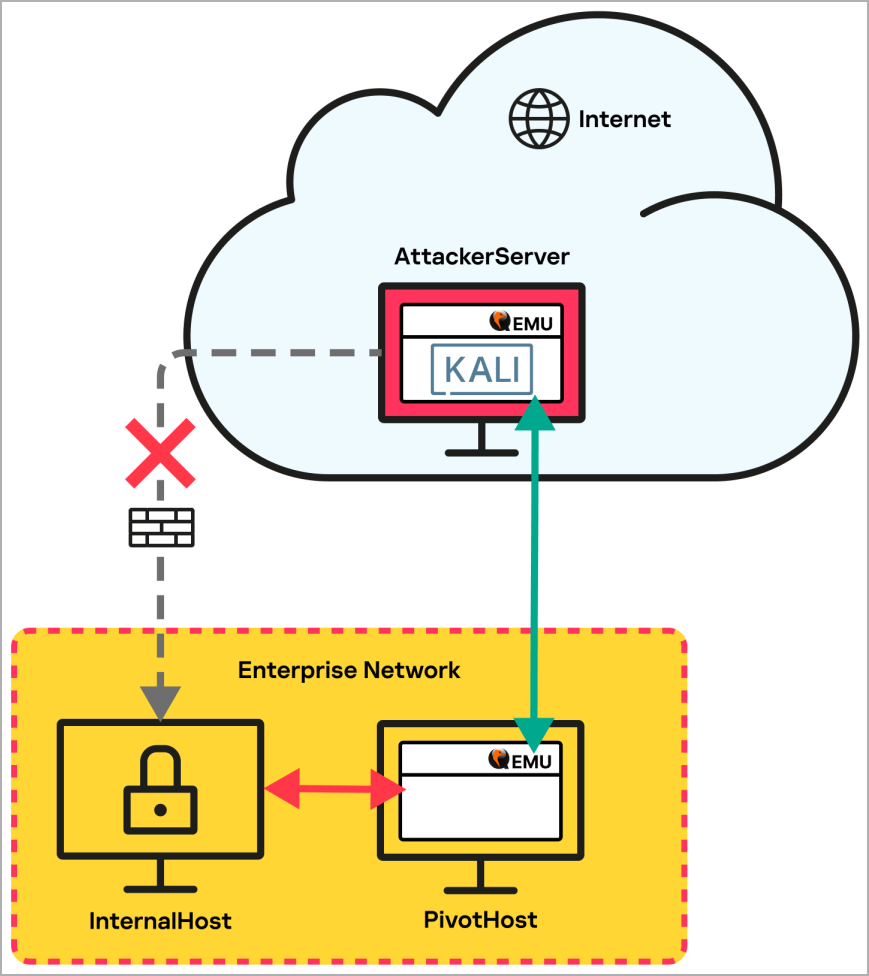
Utilizing QEMU, the attackers established a community tunnel from the focused inside host that did not have web entry to a pivot host with web entry, which in flip connects to the attacker’s server on the cloud, working a Kali Linux VM.
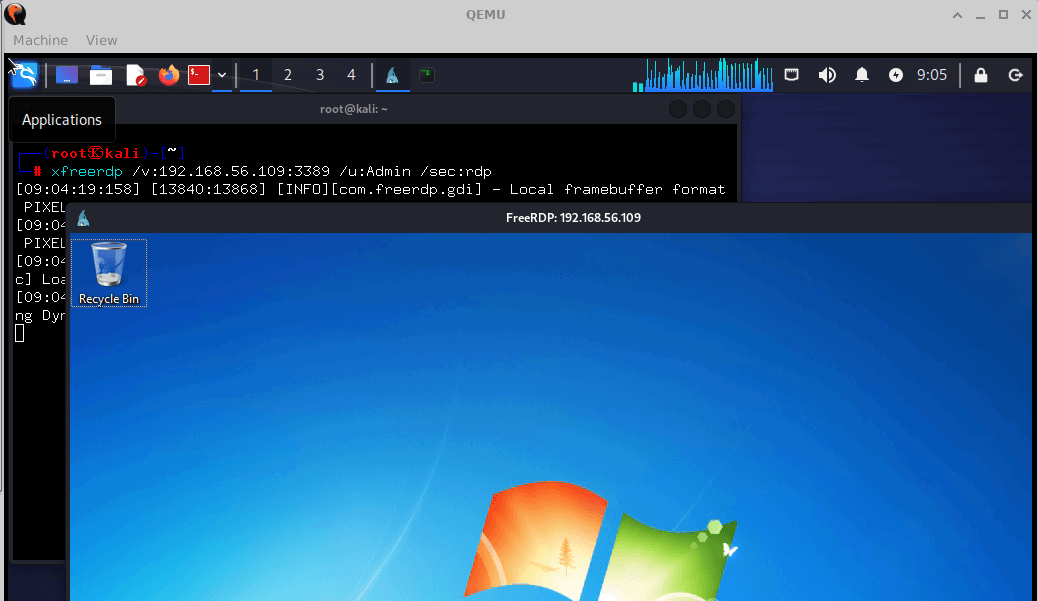
The flexibility of QEMU VMs to hyperlink seamlessly and bridge segmented community elements is essential in bypassing safety measures and can also be used to additional the breach laterally.
Kaspersky says that the enterprise ought to undertake multi-level safety to detect using professional instruments like this, together with 24/7 community monitoring, which can be outdoors the worth level for a lot of small companies.
“This additional helps the idea of multi-level safety, which covers each dependable endpoint safety, and specialised options for detecting and defending in opposition to advanced and focused assaults together with human-operated ones,” concluded Kaspersky.
“Solely complete safety that features 24/7 community (NDR, NGFW) and endpoint (EDR, EPP) monitoring, by SOC consultants for one, can detect anomalies in a well timed method and block an assault in its preliminary stage.”







