AVFoundation works on Apple’s total product line. With this framework, you possibly can add recording, enhancing, and playback options to your apps. On this article, I’ll present learn how to place one video over one other and thus allow a picture-in-picture (“duet”) mode – one of the crucial in style TikTok-like options. We’re going to use solely the native instruments for this job.
Constructing Blocks
That is what we want for this process:
AVPlayerViewControllerpermits you to play the movies and has the UI and customary controls.AVAssetExportSessionpermits you to set the format for video export. With this, your app will save the ultimate clip to the gadget’s storage.AVMutableCompositionmight be used to handle and modify video/audio tracks.AVMutableVideoCompositionwill outline the way in which the tracks combine for every body of the ensuing video.AVMutableVideoCompositionInstructionpermits you to set the directions for the adjustments of the layers within the output video.AVMutableVideoCompositionLayerInstructionpermits altering the opacity of a sure video monitor. It additionally permits cropping and resizing the video – simply what we have to make the overlay clip small and place it on the location we wish.
On this instance, we are going to use two movies. The primary video asset is the one which might be positioned behind the opposite one and performed in full dimension. The overlay video asset might be positioned within the foreground, over the primary video asset.
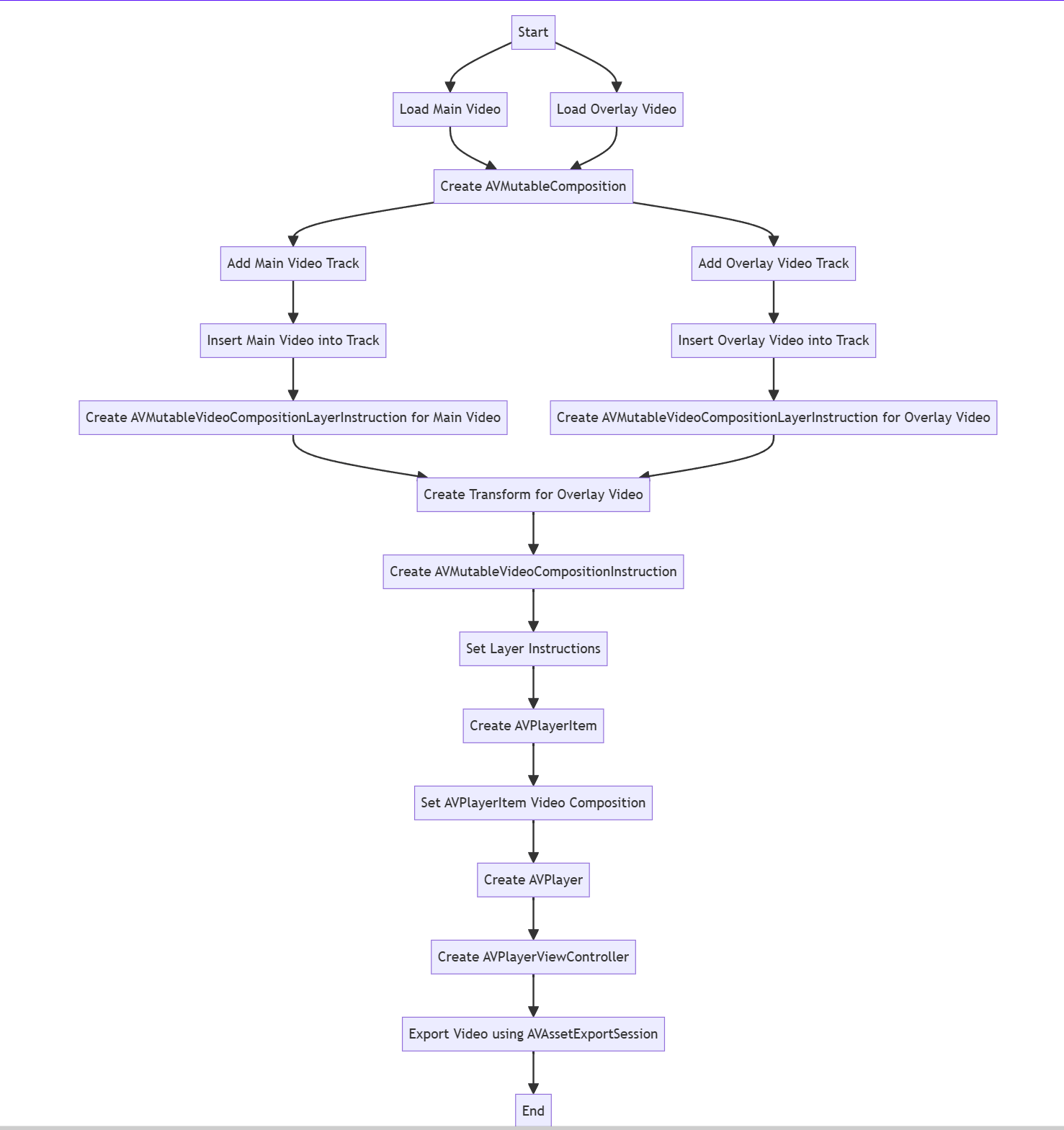
Step By Step
Begin by loading the movies. Let’s assume that they’re each positioned inside the appliance bundle as assets:
let mainVideoUrl = Bundle.important.url(forResource: "important", withExtension:
"mov")!
let overlayVideoUrl = Bundle.important.url(forResource: "overlay",
withExtension: "mov")!
let mainAsset = AVURLAsset(url: mainVideoUrl)
let overlayAsset = AVURLAsset(url: overlayVideoUrl)There are two movies, so make two clean tracks in AVMutableComposition and the suitable composition:
let mutableComposition = AVMutableComposition()
guard let mainVideoTrack =
mutableComposition.addMutableTrack(withMediaType: AVMediaType.video,
preferredTrackID: kCMPersistentTrackID_Invalid),
let overlayVideoTrack =
mutableComposition.addMutableTrack(withMediaType: AVMediaType.video,
preferredTrackID: kCMPersistentTrackID_Invalid) else {
// Deal with error
return
}The following step is to position the tracks from AVURLAsset into the composition tracks:
let mainAssetTimeRange = CMTimeRange(begin: .zero, length:
mainAsset.length)
let mainAssetVideoTrack = mainAsset.tracks(withMediaType:
AVMediaType.video)[0]
attempt mainVideoTrack.insertTimeRange(mainAssetTimeRange, of:
mainAssetVideoTrack, at: .zero)
let overlayedAssetTimeRange = CMTimeRange(begin: .zero, length:
overlayAsset.length)
let overlayAssetVideoTrack = overlayAsset.tracks(withMediaType:
AVMediaType.video)[0]
attempt overlayVideoTrack.insertTimeRange(overlayedAssetTimeRange, of:
overlayAssetVideoTrack, at: .zero)Then make two cases of AVMutableVideoCompositionLayerInstruction:
let mainAssetLayerInstruction =
AVMutableVideoCompositionLayerInstruction(assetTrack: mainVideoTrack)
let overlayedAssetLayerInstruction =
AVMutableVideoCompositionLayerInstruction(assetTrack: overlayVideoTrack)Now use the setTransform methodology to shrink the overlay video and place it the place you want it to be. On this case, we are going to make it 50% smaller than the primary video in each dimensions, so we are going to use identification remodel scaled by 50%. Utilizing the remodel, we may even alter the place of the overlay.
let naturalSize = mainAssetVideoTrack.naturalSize
let halfWidth = naturalSize.width / 2
let halfHeight = naturalSize.peak / 2
let topLeftTransform: CGAffineTransform = .identification.translatedBy(x: 0, y: 0).scaledBy(x: 0.5, y: 0.5)
let topRightTransform: CGAffineTransform = .identification.translatedBy(x: halfWidth, y: 0).scaledBy(x: 0.5, y: 0.5)
let bottomLeftTransform: CGAffineTransform = .identification.translatedBy(x: 0, y: halfHeight).scaledBy(x: 0.5, y: 0.5)
let bottomRightTransform: CGAffineTransform = .identification.translatedBy(x: halfWidth, y: halfHeight).scaledBy(x: 0.5, y: 0.5)
overlayedAssetLayerInstruction.setTransform(topRightTransform, at: .zero)Be aware that on this instance, each movies are within the 1920×1080. If the resolutions differ, the calculations should be adjusted.
Now create AVMutableComposition and AVMutableVideoComposition. You have to them to play and export the video.
let instruction = AVMutableVideoCompositionInstruction()
instruction.timeRange = mainAssetTimeRange
instruction.layerInstructions = [overlayedAssetLayerInstruction,
mainAssetLayerInstruction]
mutableComposition.naturalSize = naturalSize
mutableVideoComposition = AVMutableVideoComposition()
mutableVideoComposition.frameDuration = CMTimeMake(worth: 1, timescale:
30)
mutableVideoComposition.renderSize = naturalSize
mutableVideoComposition.directions = [instruction]The output video with the picture-in-picture mode enabled might be performed by AVPlayerViewController. First, create a brand new occasion of AVPlayer and cross it as a reference to AVPlayerItem that can use AVMutableVideoComposition and AVMutableComposition that you simply made earlier.
Should you get the “Can’t discover ‘AVPlayerViewController‘ in scope” error, you forgot to import the AVKit framework in your supply file.
let playerItem = AVPlayerItem(asset: mutableComposition)
playerItem.videoComposition = mutableVideoComposition
let participant = AVPlayer(playerItem: playerItem)
let playerViewController = AVPlayerViewController()
playerViewController.participant = participantNow that you’ve the participant, you’ve gotten two choices:
- Fullscreen mode: Use
UIViewControllerstrategies likecurrent(). - According to different views: Use APIs like
addChild()anddidMove(toParent:).
And eventually, we have to export the video with AVAssetExportSession:
guard let session = AVAssetExportSession(asset: mutableComposition,
presetName: AVAssetExportPresetHighestQuality) else {
// Deal with error
return
}
let tempUrl =
FileManager.default.temporaryDirectory.appendingPathComponent("
(UUID().uuidString).mp4")
session.outputURL = tempUrl
session.outputFileType = AVFileType.mp4
session.videoComposition = mutableVideoComposition
session.exportAsynchronously {
// Deal with export standing
}That is what it’s best to get in the long run:
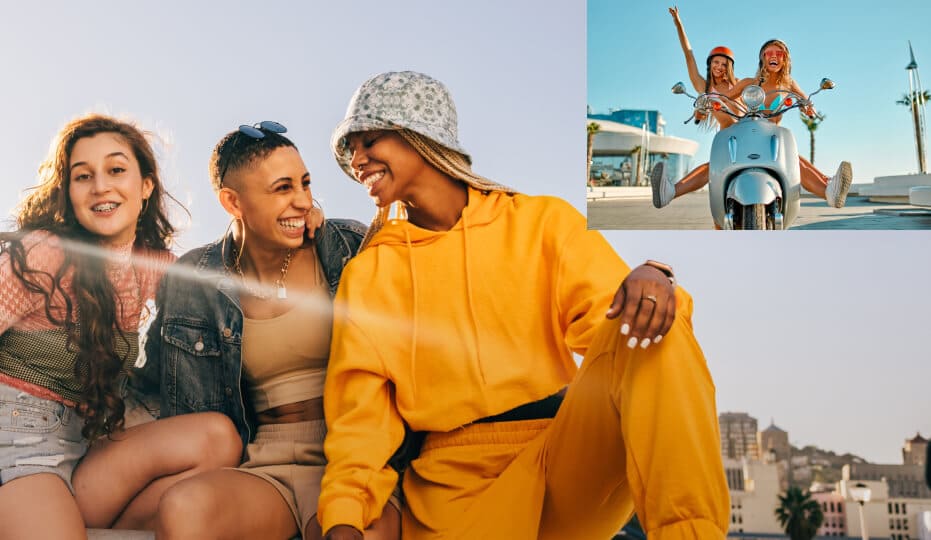

You too can modify the ultimate video, e.g. spherical out the sides, add shadow, or a coloured border. To do this, create a customized compositor class for the AVVideoCompositing protocol and a corresponding instruction for AVVideoCompositionInstructionProtocol.







