
The Iranian-backed MuddyWatter hacking group has partially switched to utilizing a brand new custom-tailored malware implant to steal recordsdata and run instructions on compromised methods.
Dubbed BugSleep, this new backdoor continues to be actively being developed and was found by analysts at Verify Level Analysis whereas being distributed by way of well-crafted phishing lures.
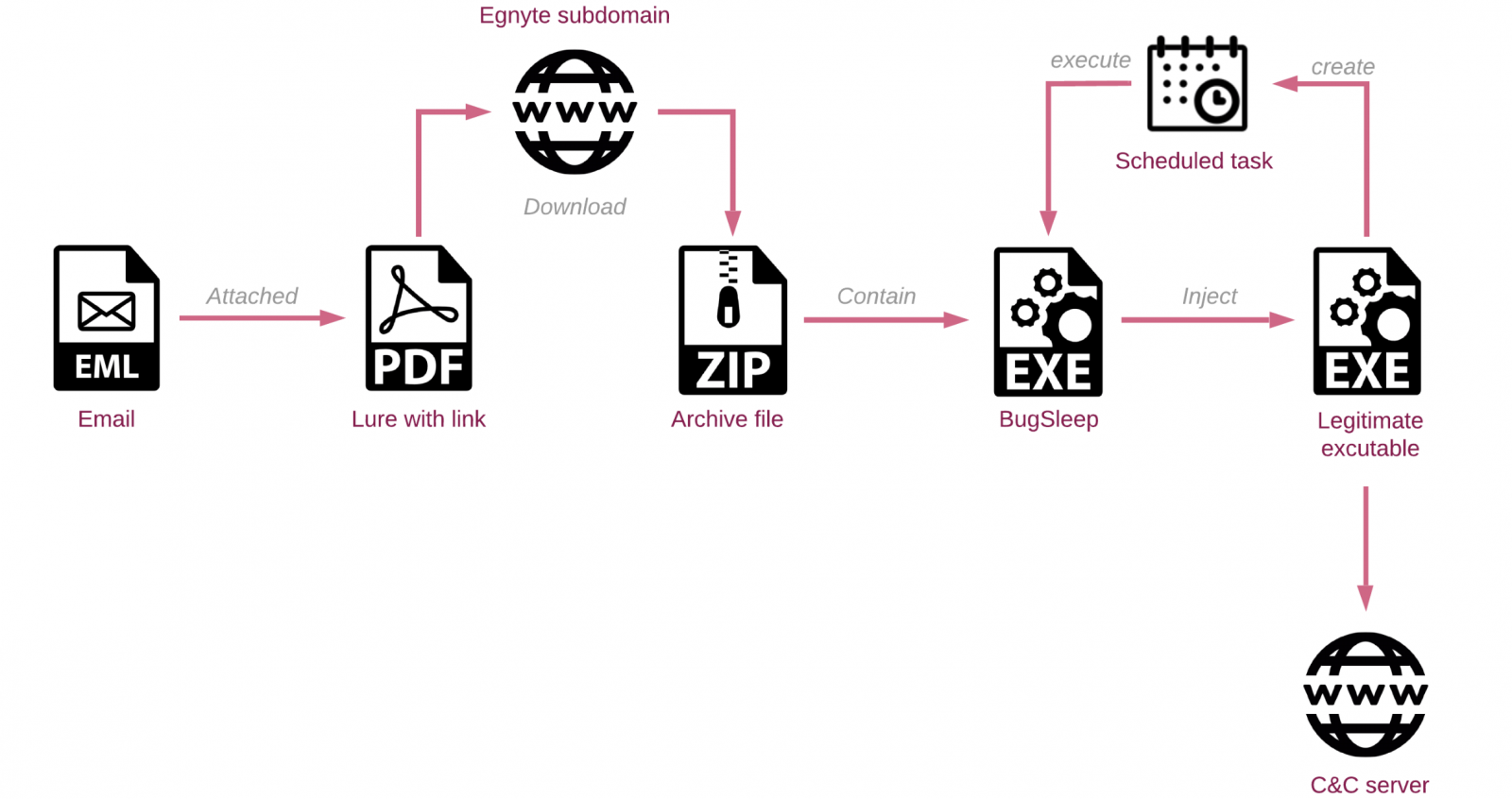
The marketing campaign pushes the malware by way of phishing emails disguised as invites to webinars or on-line programs. The emails redirect the targets to archives containing malicious payloads hosted on the Egnyte safe file-sharing platform.
Some variations discovered within the wild additionally include a {custom} malware loader designed to inject it into the lively processes of a handful of apps, together with Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, AnyDesk, Microsoft OneDrive, PowerShell, and Opera.
“We found a number of variations of the malware being distributed, with variations between every model exhibiting enhancements and bug fixes (and typically creating new bugs),” Check Point said. “These updates, occurring inside quick intervals between samples, recommend a trial-and-error method.”
With the change to BugSleep, MuddyWatter has switched from solely utilizing official Distant Administration Instruments (RMM) like Atera Agent and Display screen Join to take care of entry to victims’ networks.
Assaults utilizing this new malware concentrate on a variety of targets worldwide, from authorities organizations and municipalities to airways and media shops, with concentrating on Israel and a few in Turkey, Saudi Arabia, India, and Portugal.
Uncovered as Iranian intelligence company hackers
MuddyWatter (additionally tracked as Earth Vetala, MERCURY, Static Kitten, and Seedworm) was first seen in 2017. It’s identified for primarily concentrating on Center Japanese entities (with a concentrate on Israeli targets) and regularly upgrading its arsenal.
Though comparatively new in comparison with different state-backed hacking teams, this Iranian risk group is extremely lively and targets many trade sectors, together with telecommunications, authorities (IT providers), and oil trade organizations.
Because it surfaced, it has slowly expanded its assaults to cyber-espionage campaigns towards authorities and protection entities in Central and Southwest Asia, in addition to organizations from North America, Europe, and Asia [1, 2, 3].
In January 2022, the U.S. Cyber Command (USCYBERCOM) formally linked MuddyWatter to Iran’s Ministry of Intelligence and Safety (MOIS), the nation’s main authorities intelligence company.
One month later, U.S. and U.Ok. cybersecurity and legislation enforcement companies exposed additional MuddyWater malware, a brand new Python backdoor dubbed Small Sieve deployed to take care of persistence and evade detection in compromised networks.








