
Google is testing a brand new function to stop malicious public web sites from pivoting by means of a consumer’s browser to assault units and companies on inner, non-public networks.
Extra merely, Google plans to stop unhealthy web sites on the web from attacking a customer’s units (like printers or routers) in your house or in your pc. Individuals normally think about these units secure as they don’t seem to be straight related to the web and are protected by a router.
“To stop malicious web sites from pivoting by means of the consumer agent’s community place to assault units and companies which fairly assumed they had been unreachable from the Web at massive, by advantage of residing on the consumer’s native intranet or the consumer’s machine,” Google described the thought in a assist doc.
Block unsafe requests to inner networks
The proposed “Personal Community Entry protections” function, which might be in a “warning-only” mode in Chrome 123, conducts checks earlier than a public web site (known as “website A”) directs a browser to go to one other website (known as “website B”) inside the consumer’s non-public community.
The checks embody verifying if the request comes from a safe context and sending a preliminary request to see if website B (e.g. HTTP server operating on loopback tackle or router’s net panel) permits entry from a public web site by means of particular requests known as CORS-preflight requests.
Not like present protections for subresources and employees, this function focuses particularly on navigation requests. Its major function is to defend customers’ non-public networks from potential threats.
In an instance offered by Google, the builders illustrate an HTML iframe on a public web site that performs a CSRF assault that adjustments the DNS configuration of a customer’s router on their native community.
<iframe href="https://admin:admin@router.native/set_dns?server1=123.123.123.123">
</iframe>
Below this new proposal, when the browser detects {that a} public website makes an attempt to connect with an inner gadget, the browser will ship a preflight request to the gadget first.
If there is no such thing as a response, the connection might be blocked. Nevertheless, if the interior gadget responds, it might inform the browser whether or not the request must be allowed utilizing an ‘Access-Control-Request-Private-Network‘ header.
This enables requests to units on an inner community to be robotically blocked until the gadget explicitly permits the connection from public web sites.
Whereas within the warning stage, even when the checks fail, the function will not block the requests. As an alternative, builders will see a warning within the DevTools console, giving them time to regulate earlier than stricter enforcement begins.
Nevertheless, Google warns that even when a request is blocked, an automated reload by the browser will permit the request to undergo, as it could be seen as an inner => inner connection.
“Personal Community Entry protections won’t apply on this case because the function was designed to guard customers’ non-public community from more-public net pages,” warns Google.
To stop this, Google proposes to dam auto-reloading of a web page if the Personal Community Entry function beforehand blocked it.
When this occurs, the online browser will show an error message stating that you could permit the request to undergo by manually reloading the web page, as proven under.
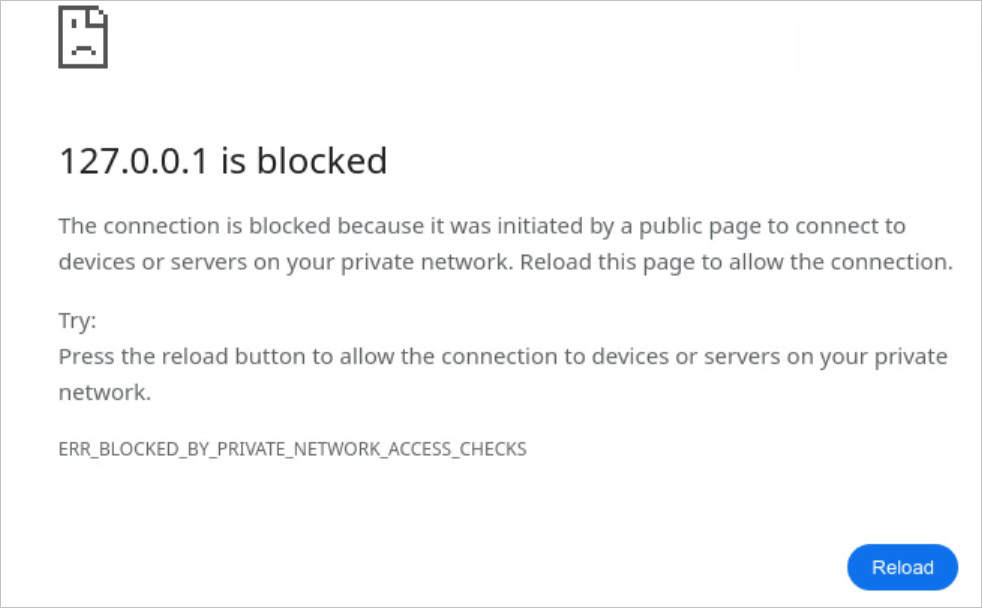
Supply: Google
This web page would come with a brand new Google Chrome error message, “BLOCKED_BY_PRIVATE_NETWORK_ACCESS_CHECKS,” to let you know when a web page cannot load as a result of it did not move Personal Community Entry safety checks.
The concept behind the safety improve
The motivation behind this growth is to stop malicious web sites on the web from exploiting flaws on units and servers in customers’ inner networks, which had been presumed secure from internet-based threats.
This consists of defending in opposition to unauthorized entry to customers’ routers and software program interfaces operating on native units—a rising concern as extra functions deploy net interfaces assuming nonexistent protections.
In accordance with a support document, Google began exploring this concept in 2021 to stop exterior web sites from making dangerous requests to assets inside the non-public community (localhost or a non-public IP tackle).
Whereas the fast objective is to mitigate dangers like these from “SOHO Pharming” assaults and CSRF (Cross-Web site Request Forgery) vulnerabilities, the specification doesn’t purpose to safe HTTPS connections for native companies—a crucial step for integrating public and personal assets securely however past the present scope of the specification.







