Entropy, the quantity of molecular dysfunction, is produced in a number of programs however can’t be measured instantly. An equation developed by researchers at Chalmers College of Technology in Sweden, and Heinrich Heine College Düsseldorf, now sheds new mild on how entropy is produced on a really quick time scale in laser excited supplies.
“New computational fashions give us new analysis alternatives. Extending thermodynamics for ultrashort excitations will present novel insights into how supplies operate on the nanoscale,” says Matthias Geilhufe, Assistant Professor on the Division of Physics at Chalmers College of Technology.
Entropy is a measure of irreversibility and dysfunction and is central in thermodynamics. Two centuries in the past, it was a part of a conceptual breakthrough, constructing the theoretical framework for machines, basic for the economic revolution. At this time, we’re seeing advances in new areas of nano and quantum gadgets, however nonetheless, entropy is a pivotal idea.
“A system often needs to evolve to a state with massive dysfunction, i.e. most entropy. It may be in comparison with a sugar dice dissolving in a glass. Whereas the sugar dissolves, the system composed of water and sugar slowly will increase its entropy. The reverse course of—a spontaneous formation of a sugar dice—is rarely noticed,” says Matthias Geilhufe.
A computational mannequin for entropy
“If we flip to how entropy is fashioned in gadgets, all of them have to be turned on and off, or want to maneuver one thing from A to B. As a consequence, entropy is produced. In some instances, we want to decrease the entropy manufacturing, for instance to keep away from data loss,” says Matthias Geilhufe.
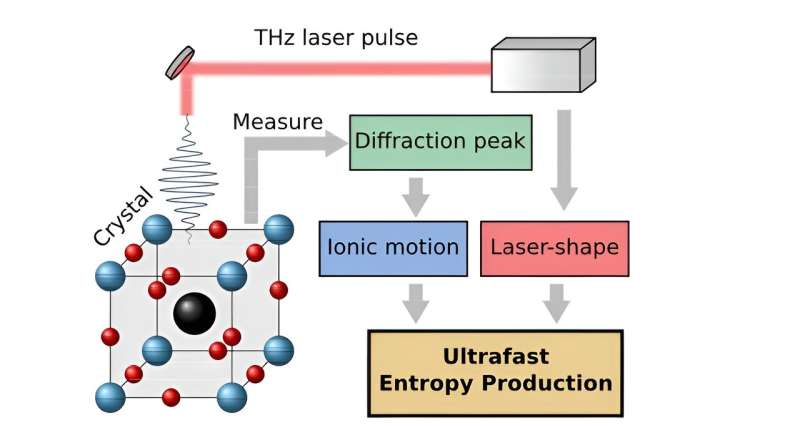
Whereas entropy has change into a well-established idea, it can’t be measured instantly. Nonetheless, Matthias Geilhufe along with researchers Lorenzo Caprini and Hartmut Löwen at Heinrich Heine College Düsseldorf, have developed a computational mannequin to measure entropy manufacturing on a really quick time scale in laser excited crystalline supplies. Their paper, “Ultrafast entropy production in pump-probe experiments,” was revealed in Nature Communications.
Phonons in crystalline supplies can produce entropy
Crystalline supplies are important for numerous applied sciences that switch and retailer data over quick durations, reminiscent of semiconductors in computer systems or magnetic storage areas. These supplies are made up of a daily crystalline lattice, whereby atoms prepare in repeating patterns.
Laser mild can shake the atoms right into a collective movement which physicists name phonons. Astonishingly, phonons usually behave as in the event that they have been a particle. They’re referred to as quasiparticles, to tell apart them from precise particles like electrons or ions.
What the researchers have now found, is that the phonons—the lattice vibrations within the crystalline materials—can produce entropy in the identical method as micro organism in water as proven by earlier analysis in organic physics by Caprini and Löwen.
By the very nature of the phonon being a quasiparticle in a crystal it may be proven that the identical mathematical sample holds as for his or her organic counterparts in water. This perception exactly determines the entropy and warmth manufacturing in laser excited supplies and permits us to know and even change their properties on demand.
The researchers’ computational model can be utilized to different kinds of materials excitations and thus opens a brand new perspective within the subject of analysis on ultrafast supplies.
“In the long term, this data might be helpful for tailoring future applied sciences, or result in new scientific findings,” says Matthias Geilhufe.
Extra data:
Lorenzo Caprini et al, Ultrafast entropy manufacturing in pump-probe experiments, Nature Communications (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44277-w
Supplied by
Chalmers University of Technology
Quotation:
New technique to measure entropy manufacturing on the nanoscale (2024, March 26)
retrieved 26 March 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-03-method-entropy-production-nanoscale.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.







