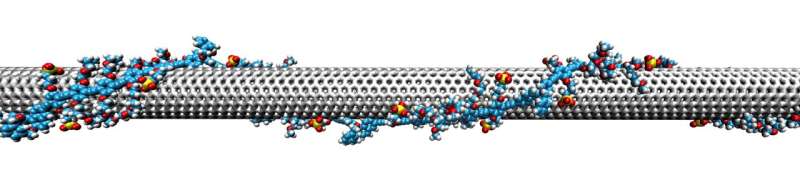
It’d appear to be a roll of rooster wire, however this tiny cylinder of carbon atoms—too small to see with the bare eye—may at some point be used for making digital gadgets starting from night time imaginative and prescient goggles and movement detectors to extra environment friendly photo voltaic cells, because of methods developed by researchers at Duke College.
Their work is published within the journal Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
First found within the early Nineteen Nineties, carbon nanotubes are created from single sheets of carbon atoms rolled up like a straw.
Carbon is not precisely a newfangled materials. All life on Earth is predicated on carbon. It is the identical stuff present in diamonds, charcoal, and pencil lead. What makes carbon nanotubes particular are their outstanding properties. These tiny cylinders are stronger than metal, and but so skinny that fifty,000 of them would equal the thickness of a human hair.
They’re additionally amazingly good at conducting electrical energy and warmth, which is why, within the push for quicker, smaller, extra environment friendly electronics, carbon nanotubes have lengthy been touted as potential replacements for silicon.
However producing nanotubes with particular properties is a problem.
Relying on how they’re rolled up, some nanotubes are thought-about metallic—that means electrons can movement by them at any power. The issue is they can not be switched off. This limits their use in digital electronics, which use electrical alerts which are both on or off to retailer binary states; similar to silicon semiconductor transistors swap between 0 and 1 bits to hold out computations.
Duke chemistry professor Michael Therien and his staff say they’ve discovered a means round this. The method takes a metallic nanotube, which at all times lets present by, and transforms it right into a semiconducting kind that may be switched on and off.
The key lies in particular polymers—substances whose molecules are hooked collectively in lengthy chains—that wind across the nanotube in an orderly spiral, “like wrapping a ribbon round a pencil,” stated first creator Francesco Mastrocinque, who earned his chemistry Ph.D. in Therien’s lab at Duke.
The impact is reversible, they discovered. Wrapping the nanotube in a polymer adjustments its digital properties from a conductor to a semiconductor. But when the nanotube is unwrapped, it goes again to its unique metallic state.
The researchers additionally confirmed that by altering the kind of polymer that encircles a nanotube, they may engineer new varieties of semiconducting nanotubes. They will conduct electrical energy, however solely when the correct amount of exterior power is utilized.
“This technique offers a delicate new software,” Therien stated. “It lets you make a semiconductor by design.”
Sensible functions of the tactic are possible far off. “We’re a great distance from making gadgets,” Therien added.
Mastrocinque and his co-authors say the work is essential as a result of it is a approach to design semiconductors that may conduct electrical energy when struck by mild of sure low-energy wavelengths which are widespread however invisible to human eyes.
Sooner or later, as an example, the Duke staff’s work may assist others engineer nanotubes that detect warmth launched as infrared radiation, to disclose folks or automobiles hidden within the shadows. When infrared mild—reminiscent of that emitted by warm-blooded animals—strikes one in every of these nanotube-polymer hybrids, it will generate an electrical sign.
Or take photo voltaic cells: This system could possibly be used to make nanotube semiconductors that convert a broader vary of wavelengths into electrical energy, to harness extra of the solar’s power.
Due to the spiral wrapper on the nanotube floor, these constructions may be best supplies for brand new types of computing and data storage that use the spins of electrons, along with their cost, to course of and carry data.
Extra data:
Francesco Mastrocinque et al, Band hole opening of metallic single-walled carbon nanotubes by way of noncovalent symmetry breaking, Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2317078121
Offered by
Duke University
Quotation:
Researchers devise new methods to engineer carbon-based semiconductors for electronics of the long run (2024, March 11)
retrieved 11 March 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-03-ways-carbon-based-semiconductors-electronics.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.







