
The North Korean APT hacking group Kimsuky is exploiting ScreenConnect flaws, notably CVE-2024-1708 and CVE-2024-1709, to contaminate targets with a brand new malware variant dubbed ToddleShark.
Kimsuky (aka Thallium and Velvet Chollima) is a North Korean state-sponsored hacking group identified for cyber espionage assaults on organizations and governments worldwide.
The risk actors are exploiting authentication bypass and distant code execution flaws disclosed on February 20, 2024, when ConnectWise urged ScreenConnect clients to immediately upgrade their servers to model 23.9.8 or later.
Public exploits for the 2 flaws have been released the next day, and hackers, including ransomware actors, shortly started leveraging them in precise assaults.
In response to an upcoming report by Kroll’s cyber-intelligence group shared with BleepingComputer, the brand new Kimsuky malware, which displays polymorphic traits, seems to have been designed for long-term espionage and intelligence gathering.
ToddleShark makes use of official Microsoft binaries to attenuate its hint, performs registry modifications to decrease safety defenses, and establishes persistent entry by means of scheduled duties, adopted by a part of continuous information theft and exfiltration.
ToddleShark particulars
Kroll’s analysts estimate that ToddleShark is a brand new variant of Kimsuky’s BabyShark and ReconShark backdoors, previously seen concentrating on authorities organizations, analysis facilities, universities, and suppose tanks in the US, Europe, and Asia.
The hackers first achieve preliminary entry to susceptible ScreenConnect endpoints by exploiting the vulnerabilities, which give them authentication bypass and code execution capabilities.
Having established a foothold, Kimsuky makes use of official Microsoft binaries, comparable to mshta.exe, to execute malicious scripts like a closely obfuscated VBS, mixing its actions with regular system processes.
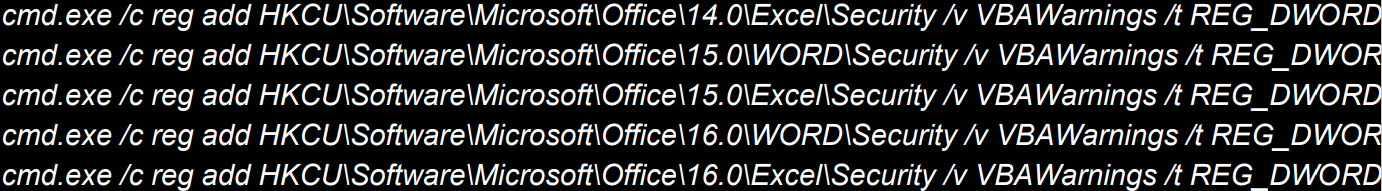
Subsequent, the malware modifications VBAWarnings keys in Home windows Registry to permit macros to run on numerous Microsoft Phrase and Excel variations with out producing notifications.
Scheduled duties are created to ascertain persistence by periodically (each minute) executing the malicious code.
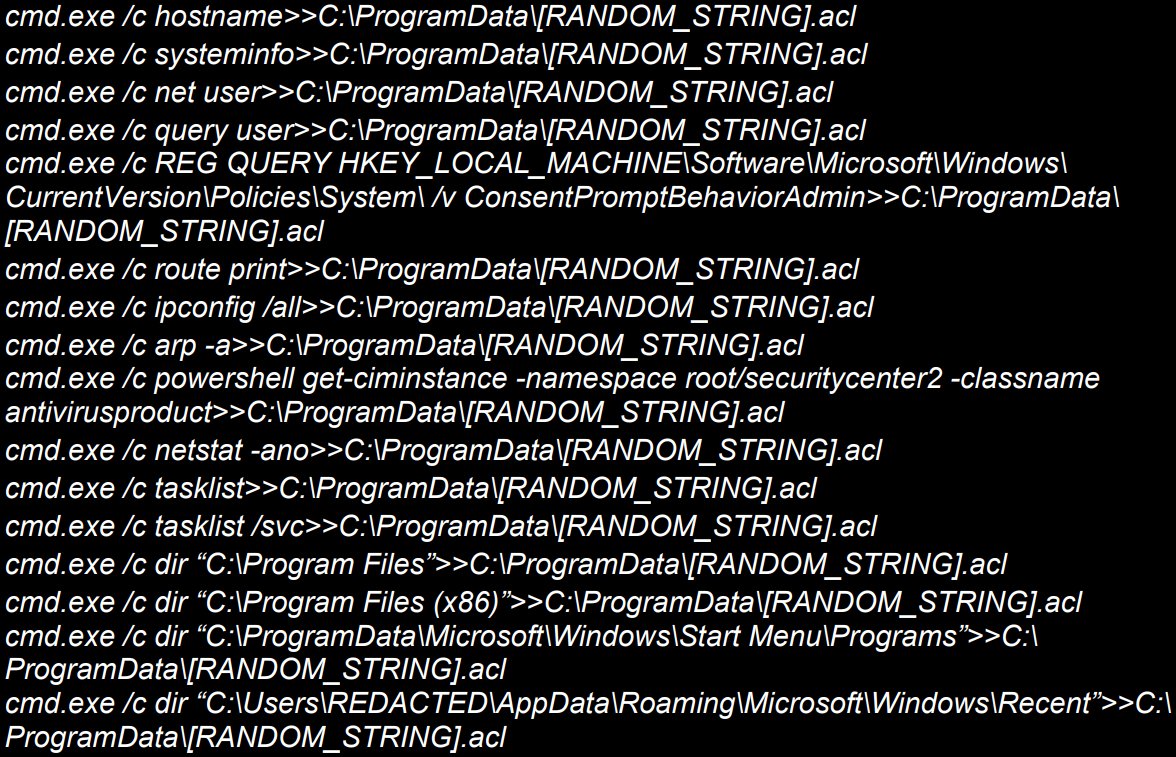
ToddleShark routinely gathers system info from contaminated units, together with the next:
- Hostname
- System configuration particulars
- Consumer accounts
- Energetic person periods
- Community configurations
- Safety software program put in
- All present community connections
- Enumeration of working processes
- Listing put in software program by parsing frequent set up paths and Home windows Begin Menu
Lastly, ToddleShark encodes the gathered info in Privateness Enhanced Mail (PEM) certificates, exfiltrated to the attacker’s command and management (C2) infrastructure, a complicated and identified Kimsuky tactic.
Polymorphic malware
A notable means of the brand new malware is polymorphism, which permits it to evade detection in lots of instances and make evaluation tougher. ToddleShark achieves this by means of a number of strategies.
First, it makes use of randomly generated capabilities and variable names within the closely obfuscated VBScript used within the preliminary an infection step, making static detection more durable. Massive quantities of hexadecimal encoded code interspersed with junk code might make the malware payload seem benign or non-executable.
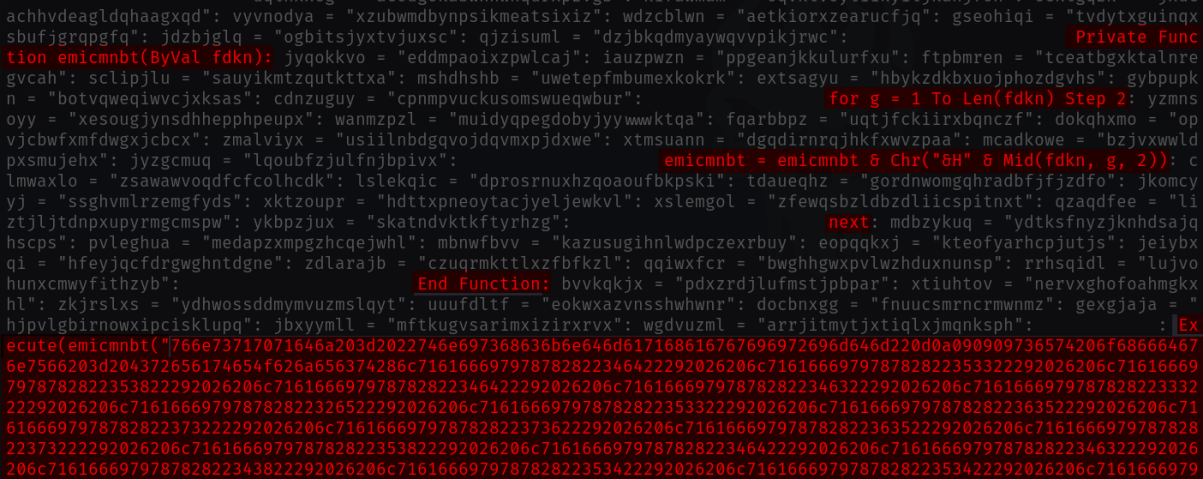
Moreover, ToddleShark employs randomized strings and [functional] code positioning, which alters its structural sample sufficient to make signature-based detection ineffective in opposition to it.
Lastly, the URLs used for downloading extra phases are dynamically generated, and the hash of the preliminary payload fetched from the C2 is all the time distinctive, so commonplace blocklisting strategies are rendered powerless.
Particular particulars and (indicators of compromise) IoCs regarding ToddleShark can be shared by Kroll through a weblog submit on its web site tomorrow.







